FAQ¶
Contact us¶
If you are still experiencing issues after reading this FAQ, feel free to contact us via any one of the following channels:
How do I reset my Portainer password?¶
At this stage, you cannot reset your password using Portainer if you have forgotten it. You can however ask another Portainer admin to reset the password for you.
There is an open feature request for this functionality which can be tracked on our GitHub repository here.
Why are my stacks showing as Limited in Portainer?¶
A Limited stack as the name implies has limited functionality. This includes browsing through to related services from the Stack Details view, or deleting the stack. A stack could show as Limited in Portainer, either because the stack was deployed outside of Portainer (Portainer doesn’t have a copy of the Stack file) or because the Portainer database has been lost (the volume it is on isn’t persisted and/or highly available).
A Total control stack in Portainer brings you added functionality such as editing and updating a stack, duplicating the stack or migrating the stack. If you wish to have a Total control stack , you will need to deploy it within Portainer so that the file is kept in the database & ensure that the database is persisted and/or highly available.
Why is my version number not matching the latest version?¶
If you have recently updated your version of Portainer, this is an indication that your browser is holding onto the previous version number of Portainer in it’s cache. To properly clear your cache, you will need to go into the browser settings and empty the cache.
Note: You can use Ctrl + shift + R on most browsers to load the specific page without cache, however you will need to repeat this on each page of Portainer to load the changes.
Can I activate my extension licenses without an internet connection?¶
Currently, it is not possible to activate extensions offline as Portainer runs a license check against our license verification server. There is a feature request open for this offline activation functionality which can be tracked on our GitHub repository here.
My licenses/extensions don’t activate, what do I do?¶
- As stated above, Portainer needs internet access to activate extensions. One way to test is to run a busybox container and see if it can reach the internet via ping or curl.
- If Portainer can reach the internet then this is not the problem. If you have access to the Portainer data filesystem you can check whether the extension binaries have been downloaded. Navigate to the filesystem in use by Portainer and check the bin directory to make sure the extension has been downloaded. If there is no extensions present, then there is an issue with Portainer downloading the extension.
- If the extensions are present, then you may have a permissions issue and they may not be able to run. Check to make sure that they are executable.
Note: Open Media Vault mounts filesystems & shared volumes with the noexec flag by default, meaning Portainer extensions can’t be enabled.
To fix this, remove noexec from the OMV_FSTAB_MNTOPS_EXT4 variable. If the filesystem or shared volume is already mounted, modify the variable in the fstab section of /etc/openmediavault/config.xml, otherwise modify the variable in /etc/default/openmediavault.
Users have access to an endpoint, but they cannot see anything. Why?¶
- By default all resources inside an endpoint are assigned to administrator only for security reasons. To give non-admin users access you can use the access control widget within each resource to assign users ownership, or you can make the resource public to give all users access.
- Alternatively, when using the Role Based Access Control (RBAC) extension you can assign users and teams a role at the endpoint level. You can read more about the RBAC extension and it’s features here.
Note: The RBAC extension requires Portainer version 1.21.0 or newer.
Portainer lost it’s configuration, why?¶
Portainer as a Container: If you have not created a persistent volume for your Portainer container, then Portainer data will be stored inside the Docker container. If the container is then restarted, you will lose all of your data.
Portainer as a Service: If you have not created a persistent volume for your Portainer service, then Portainer data will be stored inside the Docker container created by the service. If the service is updated, you may lose your Portainer configuration.
See Deployment on how to create a persistent volume. If you have a persistent volume, then the issue may be that Portainer is not constrained to the node where the data is persisted. See the below section for more info.
How do I make sure Portainer stays where my data is persisted?¶
Our recommended deployment stack file constrains Portainer to a manager node, when you have multiple managers this will potentially become a problem. Each stack or service update action could move the Portainer container between them, and you may see Portainer appear as a fresh install.
The solution is to constrain your Portainer container to the node where your Portainer data is being persisted.
- Step 1: Following deployment of our stack file you will need to find the hostname of the node where the Portainer volume is being persisted. Within Portainer, navigate to the volumes view and note down the hostname of your Portainer volume. In this example the hostname is owner.
Alternatively you can run docker node ls and note down the hostname of the node where your Portainer data is persisted.
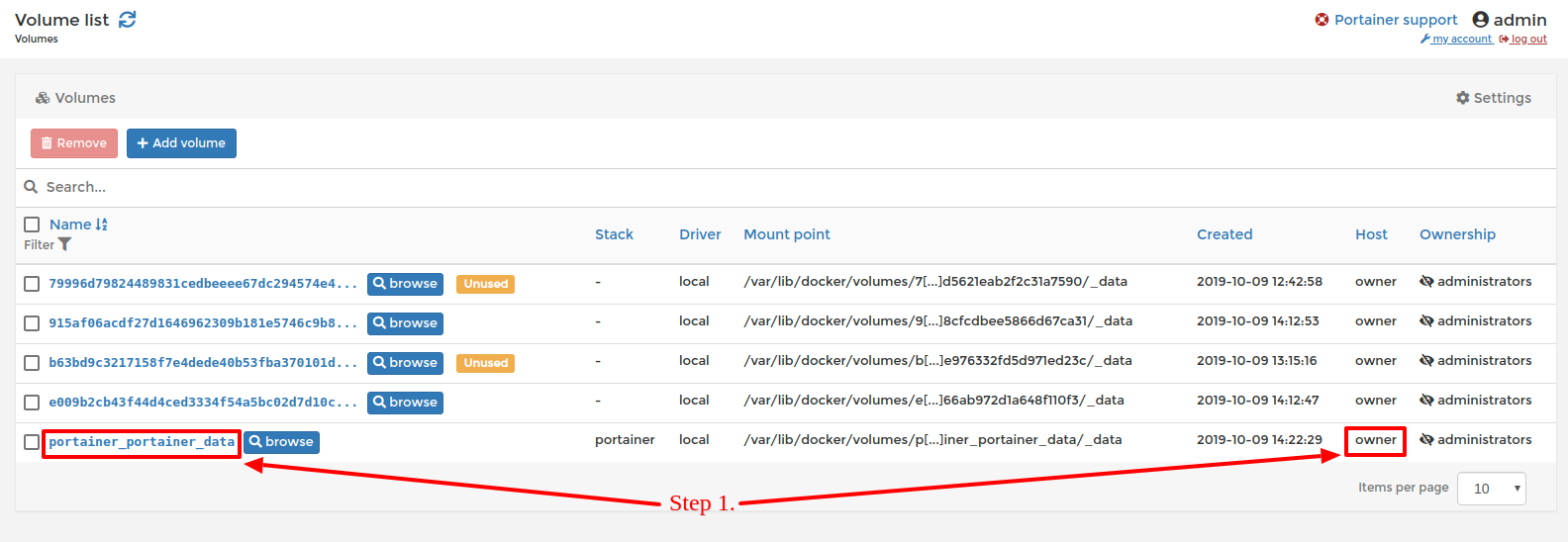
Viewing hostname of Portainer volume
- Step 2: Navigate to the Service details view for your Portainer service & navigate to placement constraints.
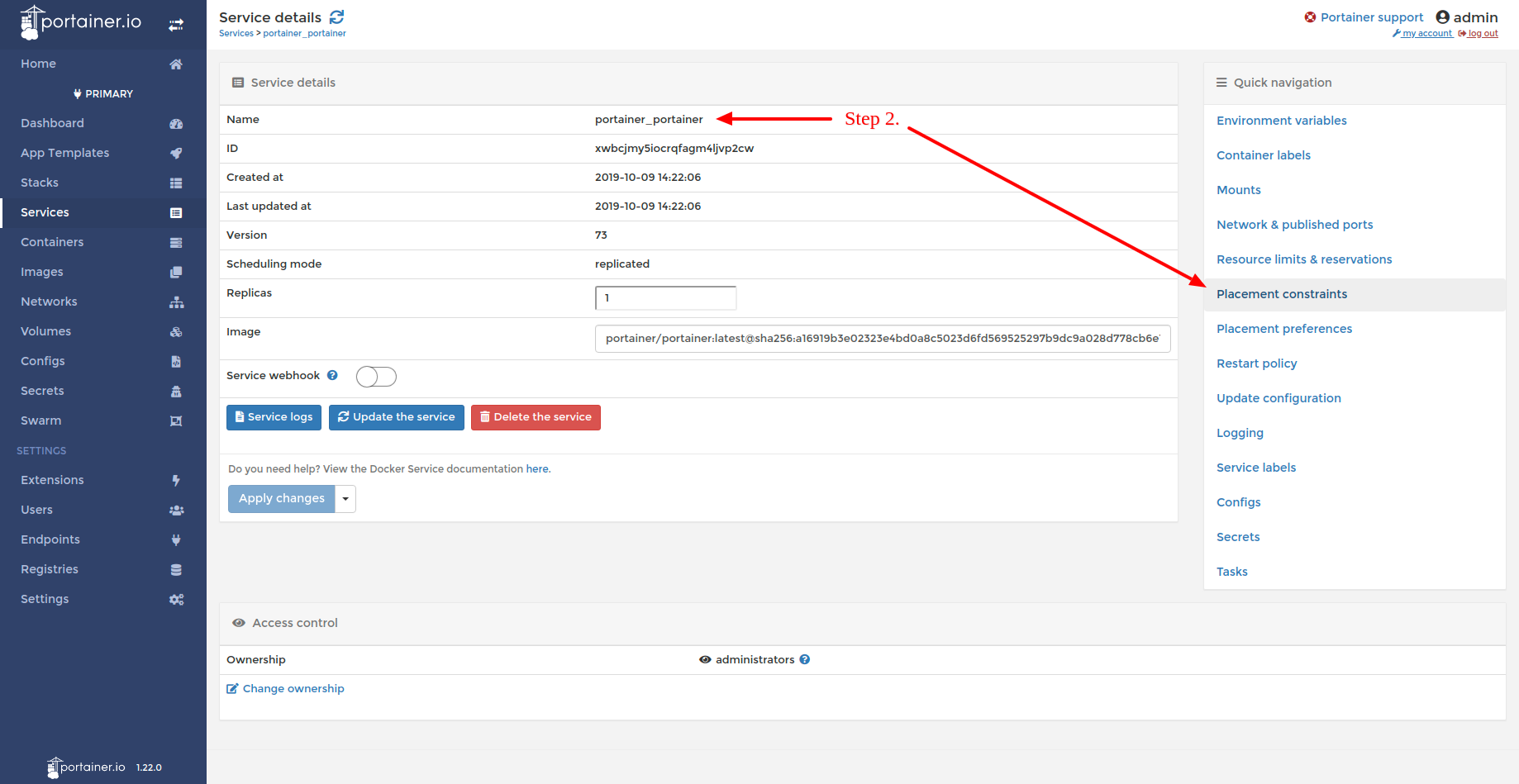
Navigating to placement constraints for your Portainer service
- Step 3: Click the placement constraints button to add a new constraint and fill in node.hostname for the name and the hostname you gathered previously for the value.
- Step 4. Click the Apply changes button to apply your constraint.
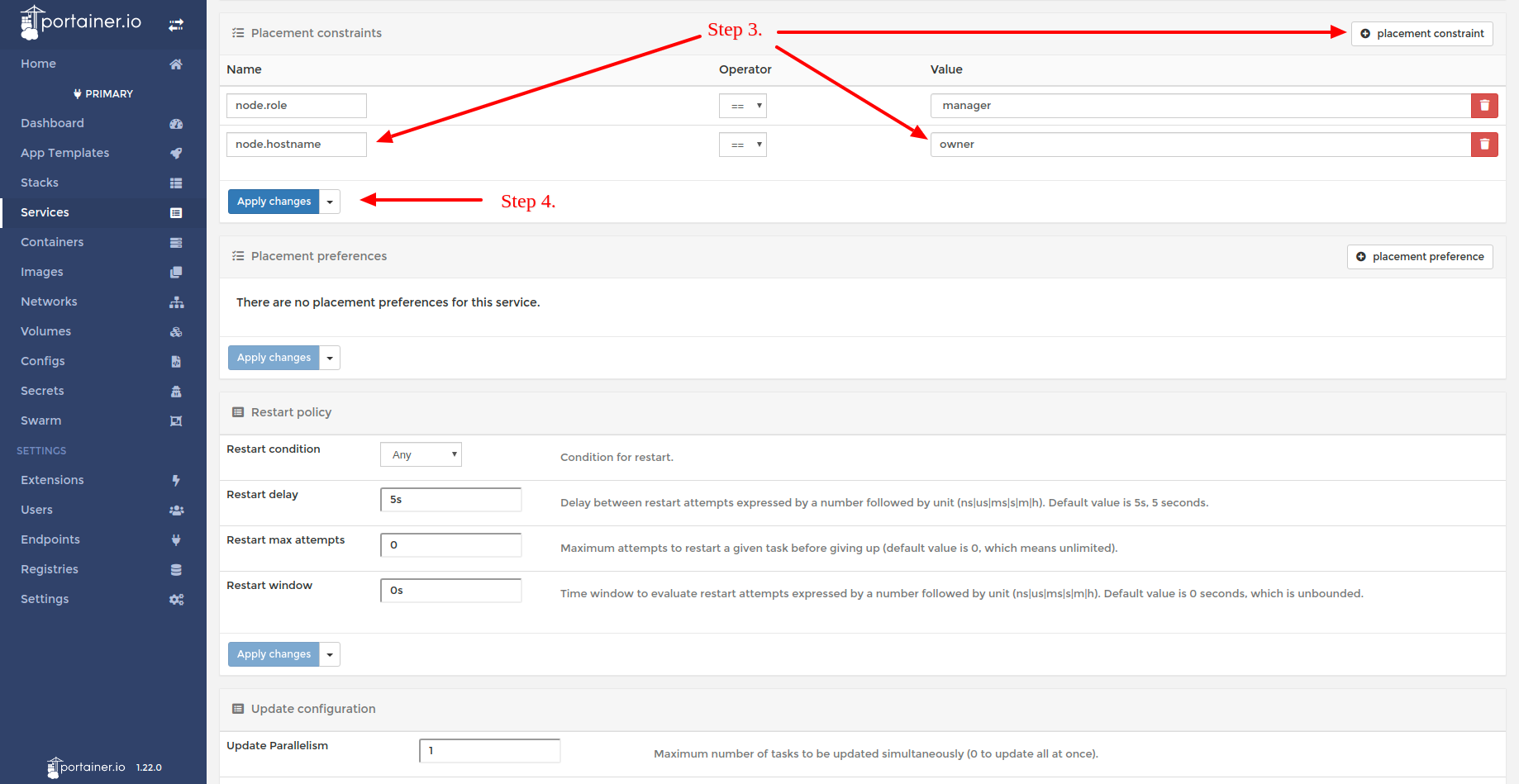
Applying the additional constraint
Why doesn’t Portainer support compose version 3 on a standalone (non-swarm) host?¶
Portainer uses the library Libcompose to deploy stacks on a standalone host, this library has been depreciated by Docker and the repository for it sits unmaintained. You can view this repository here.
How do I get the logs from Portainer?¶
You can either get the logs for Portainer from Portainer’s own GUI or from the Docker CLI on the command line.
Getting Portainer’s logs from within Portainer
- Step 1. Navigate to the Container view and click on the logs button for your Portainer container.
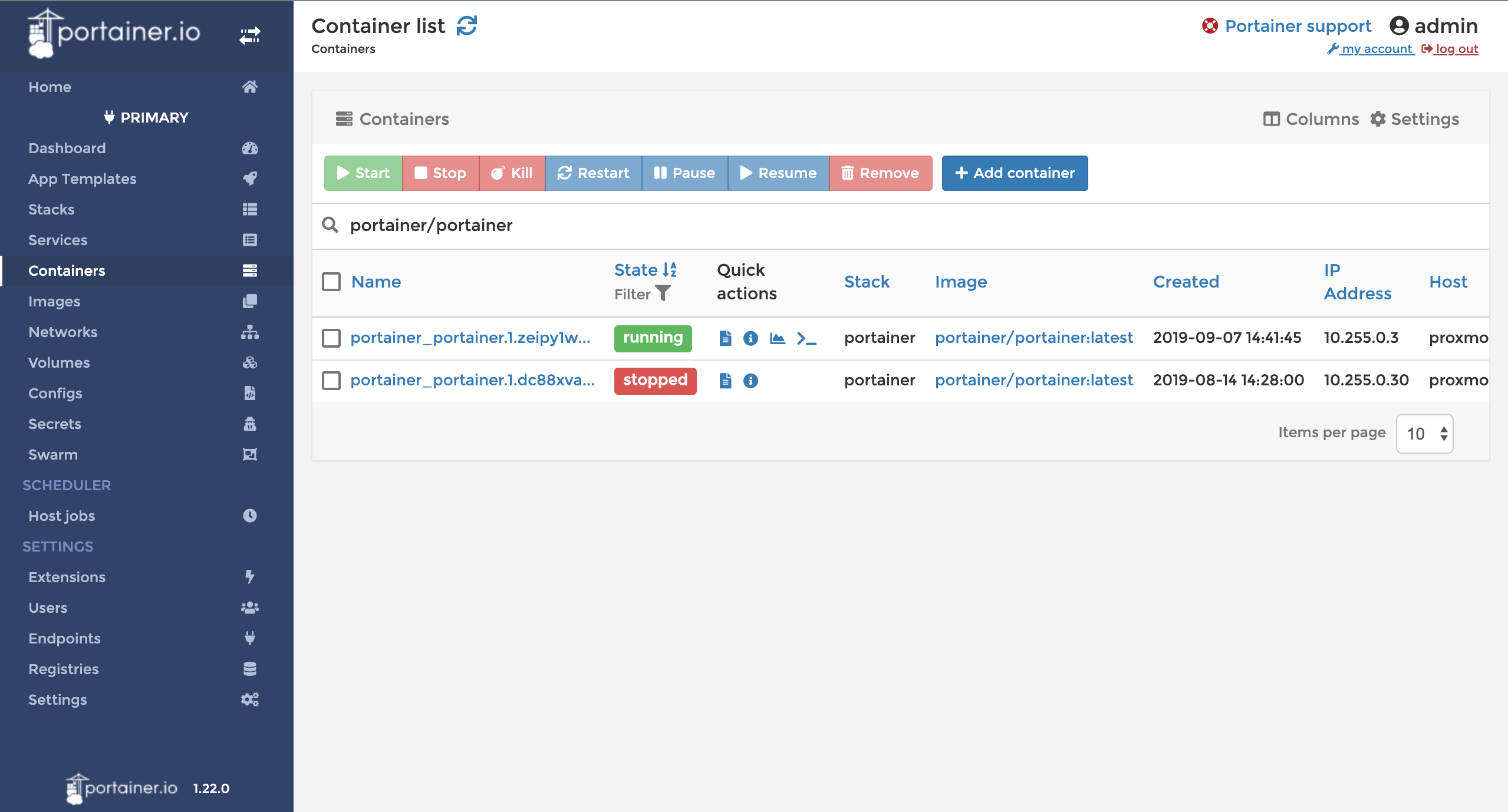
Navigating to the Container logs view for the Portainer container
- Step 2. Click on the copy button to copy the logs of the Portainer container to your clipboard.
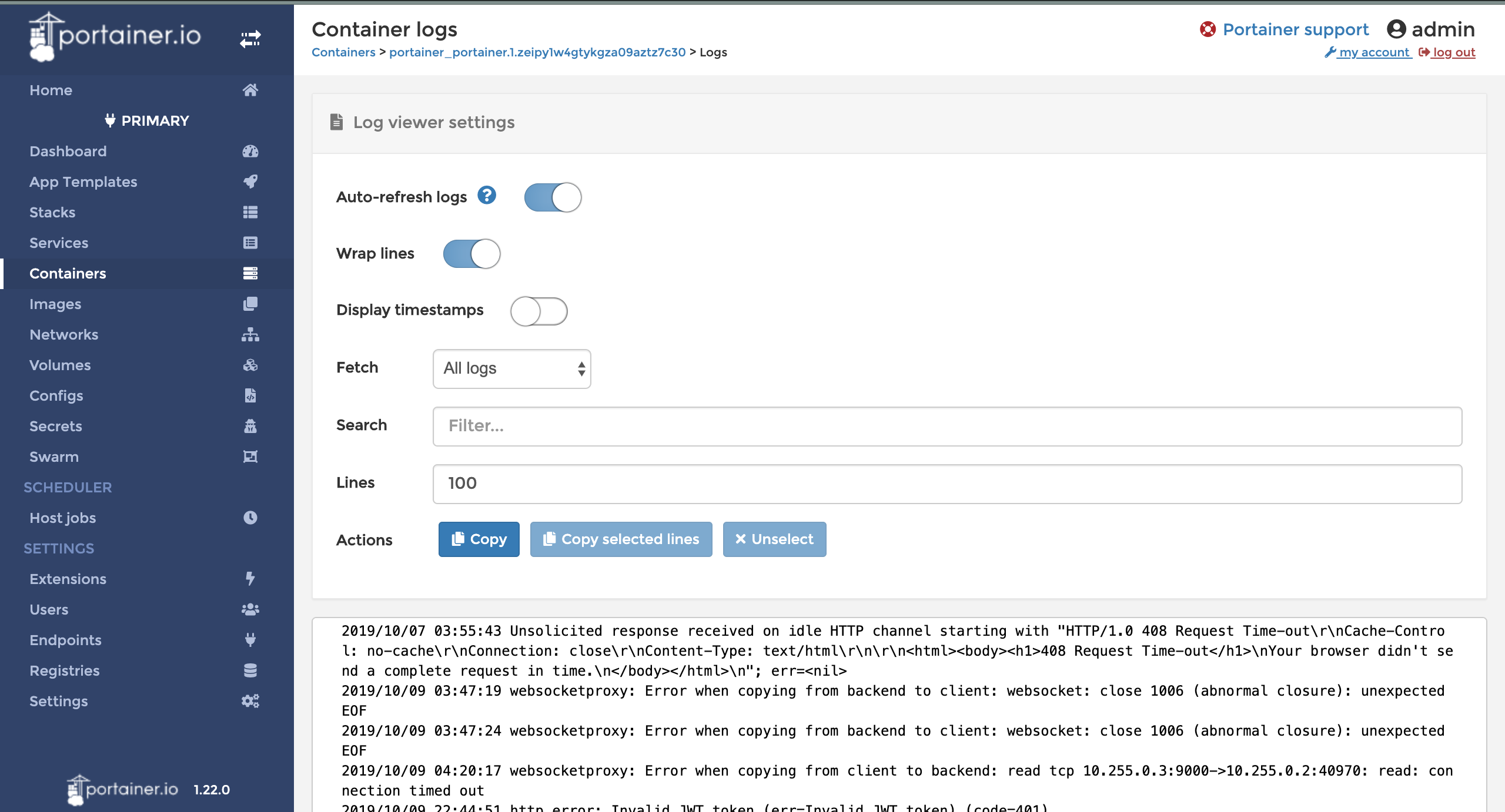
Copying the logs of the Portainer container
Getting Portainer’s logs from the Docker CLI
- Step 1. Navigate to the commandline of a Docker manager node/ non-swarm Docker host and enter
docker ps -ato list all of the Docker containers. - Step 2. Note down the CONTAINER_ID attribute of your Portainer container.
- Step 3. Enter the following command and the logs of the Portainer container will output to the commandline: docker container logs CONTAINER_ID
Published ports in the services view redirect me to about:blank#blocked, what can I do?¶
If you deployed the recommended agent stack or manage the local endpoint, you will need to set a public IP on your endpoint for published ports to work on services in Portainer.
How to set the public IP of an endpoint:
- Step 1: Go to endpoints view
- Step 2: Click on your endpoint to see it’s details
- Fill in the Public IP field for your endpoint like below:
For an agent endpoint, add the IP of one of the nodes from your cluster
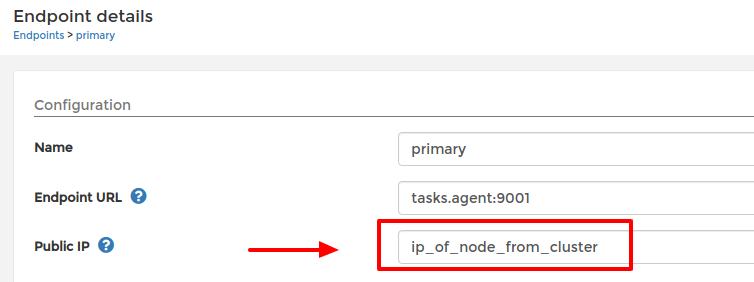
Setting public IP of Agent endpoint
For the local endpoint add the IP of the host
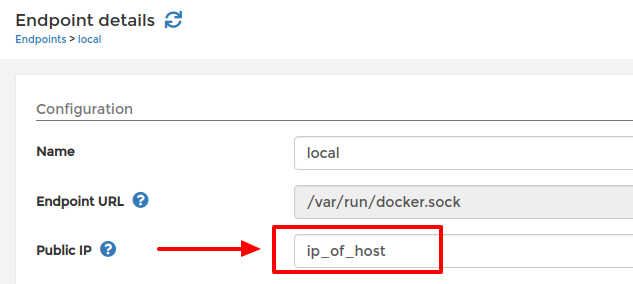
Setting public IP of local endpoint
Clicking on the published port in the Services view should now correctly redirect you to the published port of your service in the browser.
External endpoints are not working in the latest Portainer version, is this a bug?¶
We are aware that the --external-endpoint feature is not working in some of the latest versions of Portainer. If you require use of external endpoints, we recommend rolling back to Portainer version 1.21.0 until a fix has been released.
Where can I find the source code of the Portainer agent?¶
The Portainer agent is now open source! You can find it’s source code here.
My host is using SELinux, can I use Portainer ?¶
If you want to manage a local Docker environment with SELinux enabled, you’ll need to pass the --privileged flag to the Docker run command when deploying Portainer:
$ docker run -d --privileged -p 9000:9000 -p 8000:8000 --name portainer --restart always -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock -v portainer_data:/data portainer/portainer
You can also have a look at this helper: https://github.com/dpw/selinux-dockersock.
How can I use Portainer behind a proxy?¶
With Portainer behind a proxy, some features requiring access to the Internet (such as Apps Templates) might be unavailable. When running Portainer as a container, you can set the HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY env vars to specify which proxy should be used:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 -p 8000:8000 -e HTTP_PROXY=my.proxy.domain:7777 portainer/portainer
For examples on how to configure a reverse proxy to work with Portainer, you can refer to our example repo here.
Note: these are in no way production ready, and are intended solely for demonstration purposes.
How can I expose the Docker API over TCP so that Portainer can communicate with my environment?¶
Portainer strongly recommend to deploy Portainer using our agent enabled deployment due to the risk involved with exposing the Docker API. If for whatever reason it is not possible to configure Portainer with the Agent, you can configure Portainer to communicate with the Docker API over the network (usually on TCP 2375, 2376 with TLS). Refer to Daemon socket option in the Docker Reference and to Docker Engine on Windows.
How can I set up Portainer on Windows Server 2016?¶
This is a great blog post which gives instructions on how to set up Portainer on Windows Server 2016.
Note: this is applicable to Windows Server 2016 only.
How can I play with Portainer outside of the public demo?¶
You can deploy Portainer as a stack in Play-with-Docker.
Exposed ports in the container view redirects me to 0.0.0.0, what can I do?¶
In order for Portainer to be able to redirect you to your Docker host IP address and not the 0.0.0.0 address, you will have to change the configuration of your Docker daemon and add the --ip option. Note: that you will have to restart your Docker daemon for the changes to be taken in effect.
Have a look at the Docker documentation for more details.
How do I troubleshoot Portainer?¶
- Depending on your issue, make sure you first check the Portainer documentation and our user guides to ensure everything is configured correctly.
- The next thing is to check the logs of Portainer & the Portainer Agent. For instructions on how to do this, refer to the Portainer logs section above.
- If you cannot see anything wrong with your configuration or anything in the container logs, then the next step is to troubleshoot your environment.
Make sure that Docker is running with the command docker version.